Scala的核心类型,包括String,以及数值类型 Byte、Short、Int、Long、Float、Double、Char 和 Boolean。
数值类型
Byte、Short、Int、Long和Char类型统称整数类型,加上Float和Double称作数值类型。

以上列出的基本类型除了Java.lang.String外都是scala包的成员,Int的完整名称是scala.Int,不过scala包的所有成员在scala源文件中都已经自动引入,可以在任何地方使用简单名称。
以上列出的所有基础类型都可以使用字面值(literal)来书写,下图是指定字面值类型的记法:

示例:
1 | scala> val f = 1.234 |
整数类型
一些常见的整数字面值:
1 | // 如果整数以非0开头,默认被视为十进制数 |
浮点类型
浮点数以十进制数字+可选的小数点+可选的E或e打头的指数组成:
1 | // 浮点数字面值默认为Double型 |
字符类型
- 原字符表示法:使用一对单引号和中间的任意单个Unicode字符组成
1 | scala> val c = 'we' |
- Unicode字符表示法:
\u加上字符对应的四位十六进制数字,Unicode字符可以出现在Scala程序的任何位置
1 | // 出现在字面值字符中 |
- 转义字符:

String类型
Scala 本身没有 String 类,字符串的类型实际上是 java.lang.String,String 是一个不可变对象,对字符串的修改会生成一个新的字符串对象。
String字面值
- 普通字符串字面值:普通字符串字面值由用双引号括起来的字符组成,普通字符串中的
\会被解析为转义符:
1 | scala> val c1 = "hello world" |
- 原生字符串字面值:原生字符串由三重引号括起来的字符组成,原生字符串中每个字符都会被当做该字符本身进行原样输出:
1 | // 转义符会被当做普通字符 |
字符串插值
Scala默认提供了三种插值器来实现在字符串字面值中嵌入表达式,你也可以定义自己的插值器来满足不同的需求。
- s插值器:
- 语法:
s"${expression}" - 解析:
定位表达式 -> 表达式求值 -> 对值调用toString方法
- 语法:
- raw插值器:
- 语法:
raw"${expression}" - 解析:和s插值器相似,但是会把其他字符作为原义字符对待
- 语法:
- f插值器:
- 语法:
f"${expression}%.2f" - 解析:和s插值器相似,多个格式化输出
- 语法:
1 | scala> val x = 314 |
字符串的常用方法
下表列出了 java.lang.String 中常用的方法,你可以在 Scala 中使用:
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | char charAt(int index) | 返回指定位置的字符 |
| 2 | int compareTo(Object o) | 比较字符串与对象 |
| 3 | int compareTo(String anotherString) | 按字典顺序比较两个字符串 |
| 4 | int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) | 按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写 |
| 5 | String concat(String str) | 将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾,等价于 + |
| 6 | boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) | 将此字符串与指定的 StringBuffer 比较。 |
| 7 | static String copyValueOf(char[] data) | 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String |
| 8 | static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) | 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String |
| 9 | boolean endsWith(String suffix) | 测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束 |
| 10 | boolean equals(Object anObject) | 将此字符串与指定的对象比较 |
| 11 | boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | 将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写 |
| 12 | byte getBytes() | 使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中 |
| 13 | byte[] getBytes(String charsetName | 使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中 |
| 14 | void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) | 将字符从此字符串复制到目标字符数组 |
| 15 | int hashCode() | 返回此字符串的哈希码 |
| 16 | int indexOf(int ch) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 |
| 17 | int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引,从指定的索引开始搜索 |
| 18 | int indexOf(String str) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 |
| 19 | int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始 |
| 20 | String intern() | 返回字符串对象的规范化表示形式 |
| 21 | int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引 |
| 22 | int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索 |
| 23 | int lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引 |
| 24 | int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索 |
| 25 | int length() | 返回此字符串的长度 |
| 26 | boolean matches(String regex) | 告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式 |
| 27 | boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | 测试两个字符串区域是否相等 |
| 28 | boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) | 测试两个字符串区域是否相等 |
| 29 | String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) | 返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的 |
| 30 | String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement | 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串 |
| 31 | String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串 |
| 32 | String[] split(String regex) | 根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串 |
| 33 | String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串 |
| 34 | boolean startsWith(String prefix) | 测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始 |
| 35 | boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) | 测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始。 |
| 36 | CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 返回一个新的字符序列,它是此序列的一个子序列 |
| 37 | String substring(int beginIndex) | 返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串 |
| 38 | String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串 |
| 39 | char[] toCharArray() | 将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组 |
| 40 | String toLowerCase() | 使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写 |
| 41 | String toLowerCase(Locale locale) | 使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写 |
| 42 | String toString() | 返回此对象本身(它已经是一个字符串!) |
| 43 | String toUpperCase() | 使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写 |
| 44 | String toUpperCase(Locale locale) | 使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写 |
| 45 | String trim() | 删除指定字符串的首尾空白符 |
| 46 | static String valueOf(primitive data type x) | 返回指定类型参数的字符串表示形式 |
Boolean类型
Boolean类型有两个字面量,true和false:
1 | scala> val t = true |
和很多动态语言不同, Scala不支持其他类型到Boolean类型的隐式转换:
1 | scala> if(4>3) print("4>3") |
核心类型间的转换
隐式转换
- 数值类型的隐式准换:当Scala在进行赋值或者运算时,精度小的数值类型会自动转换为精度高的数值类型:
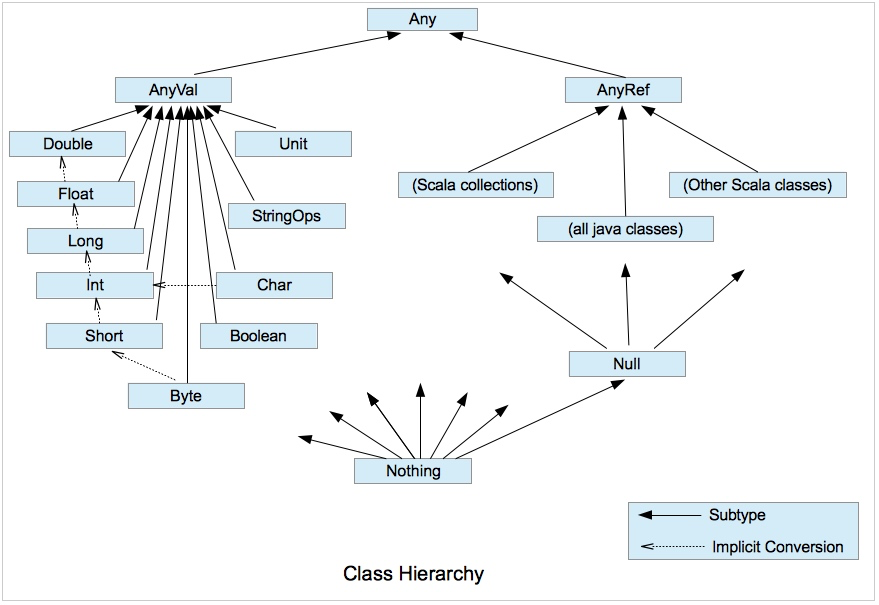
举例:
1 | scala> val a = 'a' |
- String的隐式转换:s + 会自动调用的toString方法进行字符串拼接
1 | scala> "hello" + 2019 |
显式转换
有几种方式:
- to.类型名
1 | scala> val a = 97 |
- asInstanceOf[type]:测定某个对象是否属于给定的类,用isInstanceOf方法,如果测试成功,可以用asInstanceOf方法转换
1 | scala> a.asInstanceOf[Int] |
